What is the origin of the universe? How did the universe come into being? What are the possibilities of the habitable planets in the distant cosmos? NASA launched James Webb Space Telescope on Christmas day with these lofty and outlandish ambitions. Though JWST was supposed to launch in 2010.
Moreover, the cost of JWST should have been $1 billion. There are a lot of additions of new features, the size, and the capacity of the JWST. The current cost of JWST has reached $10 billion. This is the most costly, complex, and sophisticated telescope in the history of humankind.
In 1990, NASA launched the first major optical telescope in space known as Hubble Space Telescope. Ever since, the stars, galaxies, and black holes have mesmerized and compelled scientists for further space exploration. Space exploration with the Hubble Space Telescope was limited. Whereas the JWST is a complex, sophisticated, and highly advanced telescope to explore the farthest ends of the Universe.
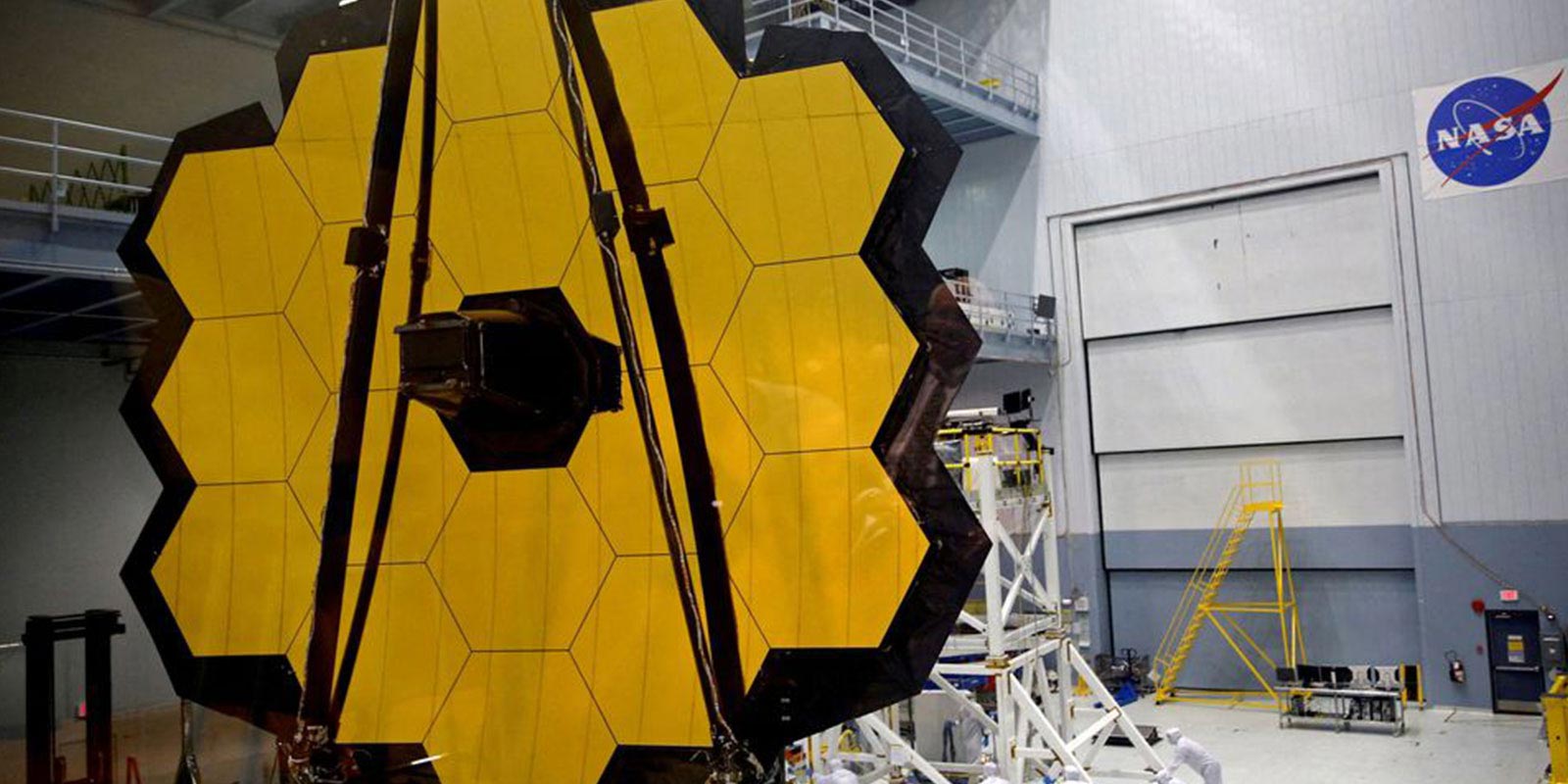
The James Webb Space Telescope is revolutionary in many aspects. Such as, it is the biggest telescope with a 21.3-foot primary mirror. Astronomers could see the edges of the universe further back into the time and creation of stars. Primarily because of the Near Infrared Cameras, JWST could see the universe beyond the comprehension of humankind.
NASA launched the JWST from French Guiana. There were many parties involved in the launching of JWST, such as the European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency. The JWST will travel millions of miles away from the earth to explore deep time, space, and the mysteries of cosmos.
Moreover, the James Webb Space Telescope can help us find new habitable planets in the infinity of the universe. In this profound article, you will know how JWST will revolutionize our understanding of the Universe.
Golden Mirror of Webb
One of the most important leaps in the development of the James Webb Space Telescope is the introduction of the miraculous golden mirror. To take clear images and seamless observations of the distant universe, galaxies, and mystical black holes, a clean environment is a prerequisite.
In the presence of pollution, haze, and dirt, images can lose their transparent appearance and outcomes can be challenging for a better understanding of observations.
To mitigate the negative effects of a polluted environment, scientists always prefer the top mountains where they can see the galaxies with no hindrance. But for NASA, no mountain is safe from obstruction and the ultimate mountain is the space itself. So, observing space from space is the best option NASA could come to.
But one question should tinker in your mind. Why does NASA have to launch a new telescope? Especially when Hubble has done too much in our primary understanding of galaxies, stars, and space? So, let’s discover what difference JWST would make and how the Hubble Space Telescope brought the rock foundations for Webb.
Contributions of Hubble Space Telescope
NASA launched the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990 with the one aim in mind that humanity needs an understanding of the universe. NASA has done astonishing progress with Hubble.
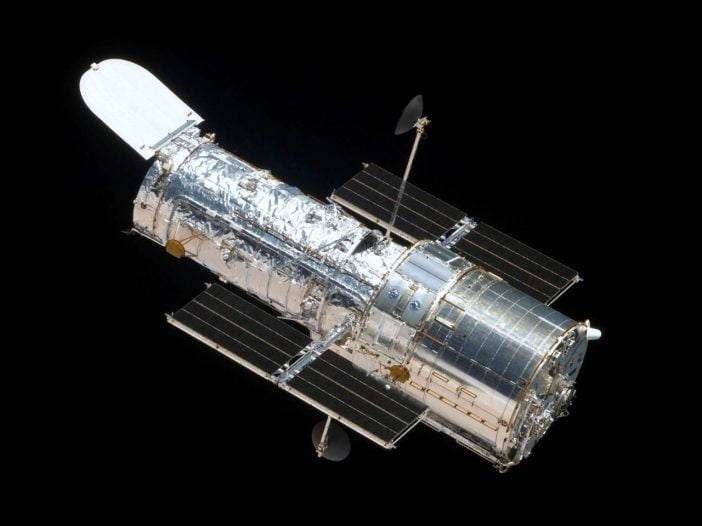

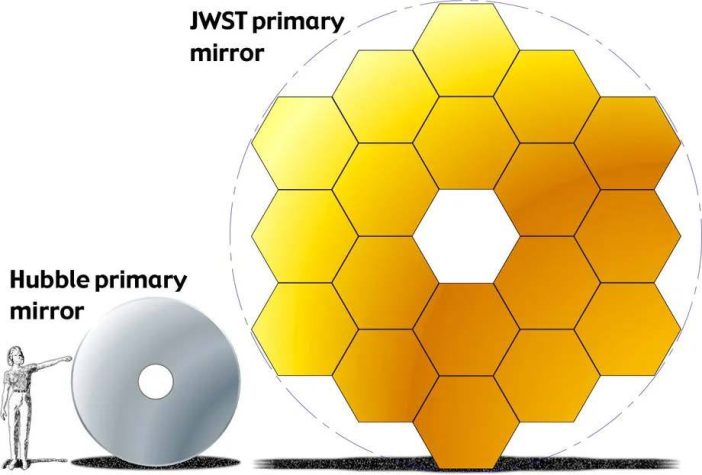
During the 30 year-run Hubble has done so much to enhance our understanding of distant galaxies, stars, and the entire universe. Despite the ordinary size of 25 feet to 32 feet and moderate mirrors of around 7.8 feet, Hubble told us about the infinity of the universe. Hubble is the pinnacle of optical and ultraviolet astronomy.
Hubble told us about the age of the universe. The telescope also discovered the two moons of Pluto. It created a 3D map of dark matter. We came to know that the universe is expanding continuously without a minor respite and that its complexity is increasing ceaselessly. The Hubble Space Telescope discovered that every major galaxy has a black hole at the center.

Moreover, we got the enthralling images of Pillars of Creation and Lagoon Nebula. Before Hubble, we were unaware of space pollution, which is commonly known as dark energy. Webb will come to extend the boundaries of Hubble and help NASA to extend them even far beyond the Hubble.
How does JWST surpass Hubble?
The James Webb Space Telescope is the sophisticated and largest telescope NASA has ever built. An astrophysicist at NASA, says “What we’re going to get is a telescope that’s about 100 times more powerful than Hubble.”
Moreover, it is so large that NASA launched JWST folded up inside a rocket. Webb’s telescope needed several weeks to unfurl the sun-shield and golden mirrors. There are many uncontroversial arguments about the supremacy of the JWST over the Hubble. One of them is the size of the JWST. Straughn said JWST is the size of a tennis ground while Hubble was the size of a school bus.
But it’s not about the size only. The James Webb Space Telescope is profound in many aspects. “The Webb represents the culmination of decades, if not centuries, of astronomy,” says Sara Seager.
It all comes down to the mirror sizes. The more light a mirror can accumulate, the more details it can capture about distant stars, galaxies, and planets. The golden mirror of JWST has 21.3 feet in diameter, which is enormous given the whole size of the telescope.
JWST and Cosmic Dark Age
Light travels and takes time to reach us. The farther an object is, the more time it would take to reach us. That’s where Webb’s telescope would make a mark. Currently, the Hubble Space Telescope could take us as far back as 400 million years after the Big Bang. However, the JWST could take us as far back as 250 million years after the Big Bang. That might not seem big, but the difference is tremendous when we see it on a timescale.
Then in the dense cloudy pollution of space, Hubble can’t take us back in time as JWST can. JWST uses the Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) to capture the images of the distance. So, the dust, stones, particles, and other hindrances are not a big deal with Webb’s telescope.
However, there are some places where even the Webb can’t reach, such as “dense, obscuring fog of primordial gas.” No light can reach a telescope through this time and that is commonly called the dark cosmic age. But some astronomers of NASA hope that the Webb would help us to understand the end of the dark cosmic age.
JWST sees Infrared Light through Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam)
For the observation of the universe, light is very important. Stars emit lights of different wavelengths. Some of them are visible to the naked eye, such as narrow-band visible light. Whereas there are plenty of light bands that are invisible to the naked human eye. We can’t see the higher frequency ultraviolet and gamma rays.
Besides, the cosmos is simmering with low-energy lights such as infrared, radio, and microwaves. We can’t see them and the first major optical telescope Hubble could also see only ultraviolet, visible light, and a tiny amount of infrared. So, most of the distant stars emit low-energy low frequency infrared light. That’s why the distant celestial bodies were hidden till now. Webb’s telescope can fill this gap efficiently.
James’s telescope is also known as an infrared telescope because it can see longer wavelengths than our eye can see. Moreover, this primary function of the James Telescope can enable astronomers and scientists to see further back into time. The gigantic universe is hilariously expansive and vast. Light is a source of measuring the depth of the universe and the mystery of creation. The longer the wavelength, the older the source.
Galaxies and black holes are millions of light-years away from us. The light that comes out from such hugely distant celestial objects expands and becomes redder. It expands into the vastness of space with longer wavelengths.
This low-energy light can give us the clue of distant space objects, their origin, and the reason for creation. Although the universe is expanding ceaselessly still with the help of Webb, we can find the source of stretched light of low energy infrared light.
Redshift and the JWST
Redshift phenomena are very important to study using the James telescope. Continuous expansion of the universe stretches the light and molds it into low-energy longer wavelength light. This ancient light grows redder and redder as it travels away from the source. This light is invisible to the naked human eye.
However, Webb can capture this light using the Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam). So, not only we can see the light, but we can also observe the redshift phenomena and how it is affecting our universe. This is ineffable and the development of the James Webb Space Telescope is a tremendous leap towards space exploration.
Is JWST a quest for a new habitable planet?
The universe is magnanimous. Only our solar system has seven planets which are revolving around a star, the sun. From the past three decades of effort, astronomers and scientists came to know that there are thousands of planets, galaxies, and solar systems. However, we could not determine whether life exists on these seemingly habitable planets. With the continuous endeavor of the past thirty years, scientists discovered around 4000 exoplanets.
Serendipitously, some of the discovered exoplanets are known to exist in the “Goldilocks Zone”. It is a moderate distance of the exoplanets not far close and far from the host star. Thus, a moderate distance enabled these exoplanets to have liquid water like earth. These are promising discoveries about the habitable planets. Yet, with the help of the Hubble Space Telescope, scientists could not find out exactly about the existence of life on these exoplanets.
The James telescope can help us find not only another planet but also life. Only in the first year, JWST will observe around 70 exoplanets that were discovered in the previous observations. With the help of the James Telescope, scientists will study them more accurately. To know about the existence of life on other planets, we need to know the chemical composition and evidence of the existence of liquid water.
Scientists like Stevenson would use the James telescope to study the atmosphere of exoplanets. JWST can analyze the chemicals in other planets such as water, CO, CO2, and methane. Although these are not the confirmed signs of life.
Still, they can raise important questions. Such as from where these gasses come from? What instigates them to exist? Such questions and a quest to find the answers can finally lead NASA’s scientists to discover the habitable planets in the far corners of the universe.
JWST is precarious yet a robust project
The Webb telescope was supposed to launch in 2010 with a $1 billion investment. However, the complexity of size, the epitome of technology, and the immense size of the mirrors delayed the project and increased the total cost to $10 billion.
Scientists are curious and immensely awaiting to join the pieces of puzzles together to solve the cosmos mystery and origin of the universe. Despite the utmost care taken, there are still many chances of failure. According to NASA, there are over 300 potential dangers to the successful launch of JWST.
And even a single technical glitch can cause utter failure. Even more astonishing is that, unlike Hubble, James’ telescope launched a million miles away from the earth. This means in case of any technical problem astronomers could not fix them. So, it is a make it or break it project. One more prominent challenge is the heat.
As JWST is ultra-sensitive to infrared light so even a tiny amount of infrared light will be visible. However, every hot surface emits infrared light. So, remaining close to the earth and sun is not a good idea for such a gigantic project.
So, NASA launched the Webb telescope into an orbit known as Lagrange point where the temperature is not high and James telescope would remain cold. This unique point is important for successful space exploration. Despite inordinate challenges, scientists are keen to see the prospects of the James Webb Space Telescope.
Wrap Up
The Hubble Space Telescope was the first hope of humanity to see beyond the earth. As time passed, the need to dig deeper into the depths of space became an essential need. To go beyond the boundaries of the Hubble, James Webb Space Telescope launched on Christmas Day. With the tremendous power of the James telescope, we can detect infrared light with a Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam).
Moreover, scientists can lead the quest to find new exoplanets in the far breaths and widths of the Universe. Sara Seager is a planetary scientist and astrophysicist at MIT who says that “We’ve been waiting for this for a very long time.”



Share Your Thoughts