It all started in a little city in China called Wuhan, where this mysterious virus, now known as coronavirus, spread fast through the world, halting life as we once knew it and endangering millions. Fast forward a few months as we now have a few promising vaccines.
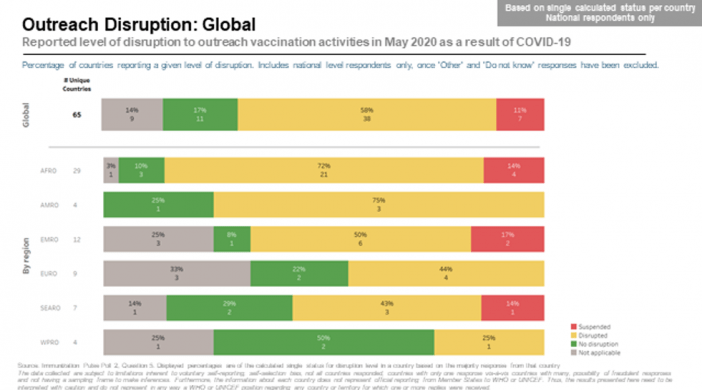
Over the course of the year, covid 19 has taken the world by storm, but a recent breakthrough in potential covid 19 vaccines has shed some hope and light on what has been a bleak and challenging year for all. One of the biggest challenges will be vaccinating the world while causing the least amount of disruption. A poll conducted by WHO (The World Health Organisation) found disruptions to routine immunization services continue to be widespread.
Positive clinical trial results from a number of vaccines created by a range of different institutions demonstrate not only how far technology itself has come but also how far science has come. Although the pandemic is far from over, the potential vaccines developed to offer a potential time frame before we can return back to our lives as normal.
Here’s a look at the most popular and sought after vaccines that could be used to help in the fight against the virus.
Moderna
The Moderna vaccine produced by a Massachusetts-based company is in its own right, not just a vaccine but also a medical breakthrough that will allow normality to return back to life. The vaccine is based on ribonucleic acid (RNA) and is a molecule that shares some similar properties to DNA and one which is created naturally by our bodies.
Vaccines most often contain either weekend viruses or purified proteins of a virus and typically train our immune systems to recognize disease-causing viruses, helping to neutralize them. The mRNA vaccine works differently because instead of receiving the viral infection directly, the person being vaccinated will receive genetic material, which is mRNA, which helps to encode the viral protein in the body.
When the genetic instructions are administered into the patient via an injection in the arm, the muscle cells will translate them to make the viral protein directly into the body. The vaccine only codes the critical parts of the viral protein, which is covid-19.
This small insight gives the body and immune system a preview of what the real virus looks like without causing the disease in the patient. Doing this allows the immune system to generate and design antibodies that are powerful and can neutralize the real viral covid-19 proteins present in the body.
The mRNA vaccine is considered to be synthetic genetic material, which means it can not be passed onto or transmitted to the next generation. Once the injections have been given, the molecules’ only job is to help guide the production of proteins in the muscle cells, after which it reaches its peak levels for 24-48 hours and can last no longer than a few days in the body.
Pfizer/ BioNTech
Pfizer and BioNTech were one of the first organizations to announce their potential vaccine for Covid-19 following the success of their early phase III trials. Similar to the Moderna vaccine, the Pfizer vaccine is also mRNA based and shows promise for working well in the elderly.
The RNA vaccine works by introducing a messenger RNA into the body like the Moderna vaccine that contains a genetic instruction for the patient vaccinated cells to begin creating vaccine antigens. These antigens will help to produce a vaccine response, thus helping to fight off the coronavirus.
One of the key issues with the Pfizer vaccines that it needs to be stored in freezing temperatures at -70 degrees celsius, this causes a range of different problems as not many GP surgeries to have fridges that store the medicine at such low temperatures making the vaccine harder to give.
The vaccine will also degrade in 5 days time at normal refrigeration temperatures, which means it has a shelf life of only five days. This is the same for the above Moderna vaccine as they both use the same type of technology and methodology.
Oxford AstraZeneca
The Oxford and AstraZeneca vaccine is built around a virus that causes the common cold in Chimpanzees. The virus that affects the chimps is modified in this vaccine, so it cannot multiply and cause the disease in the body, but rather it is loaded with the gene for the coronavirus spike protein. The small club-shaped parts that dot the surface of the virus are used to penetrate human cells.
Once the vaccine enters the body, the chimp virus delivers the coronavirus gene to a range of human cells. Once this takes over, the cells begin to release spike protein, which is then detected by the immune system.
The immune system then produces antibodies and other responses to the gene, which can help to attack the real coronavirus present in the patient if they were to become infected in the future.
The vaccine is named ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and is based on different technology compared to the previous two vaccines by Moderna and BioNTech. The Oxford vaccine and AstraZeneca vaccine is a partnership between the two organizations. Of the three vaccines, the oxford vaccines are the cheapest, and more importantly, it can be stored at a standard, workable temperature of between two to eight degrees.
However, the production of mRNA vaccines like the Pfizer and Moderna one could potentially offer a more flexible approach to the fight against covid by tackling pathogens that are rapidly evolving. This will help to offer a faster response to larger outbreaks and epidemics.
Although the vaccines have similarities and differences, the impact they have on the world at large will mean that life can return back to normal at some point. Many industries, such as the airline industry, are taking precautions and are pushing for electrical vaccine passports via smartphone to be issued to those who have been vaccinated, deeming them fit to fly. Those who can not show evidence of being vaccinated will be unable to fly.



The article starts by referring to a “little city in China called Wuhan”. Maybe this is US style humour?
Also, the choice of just 3 vaccines (2 American and 1 British) from western big-pharma further reduces credibility.